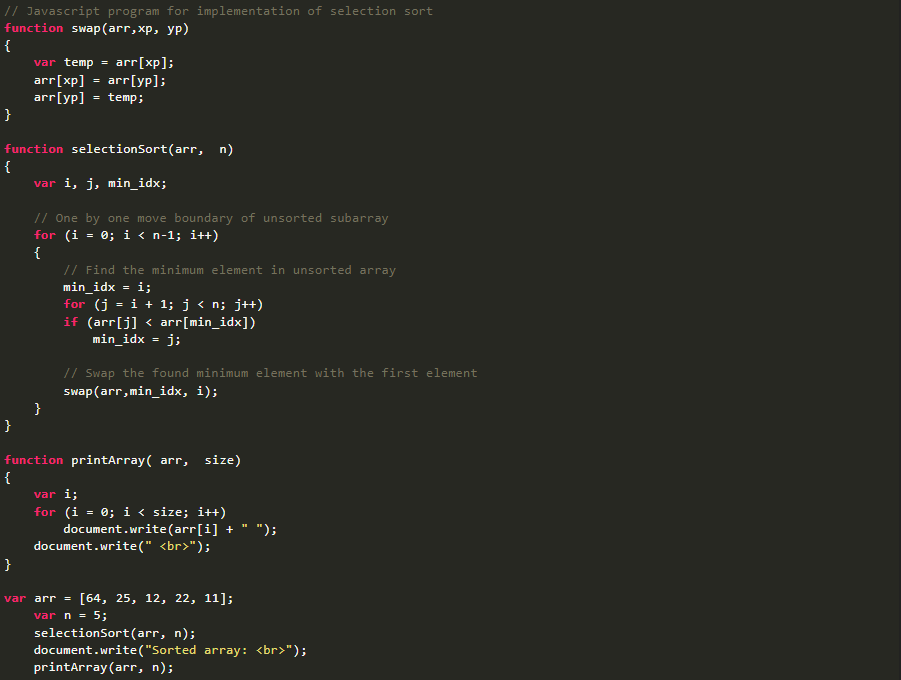
Basic Principle:
- Selection sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm.
- It repeatedly divides the input list into two sections: sorted and unsorted.
Efficiency and Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(n^2), where 'n' is the number of elements in the list.
- Its efficiency diminishes significantly with larger datasets due to its quadratic time complexity.
Iterative Process:
- Selection sort iterates through the unsorted section to find the minimum (or maximum) element.
- The smallest (or largest) element is then swapped with the first unsorted element, expanding the sorted section.
- Each iteration increases the size of the sorted section and reduces the unsorted section until the entire list is sorted
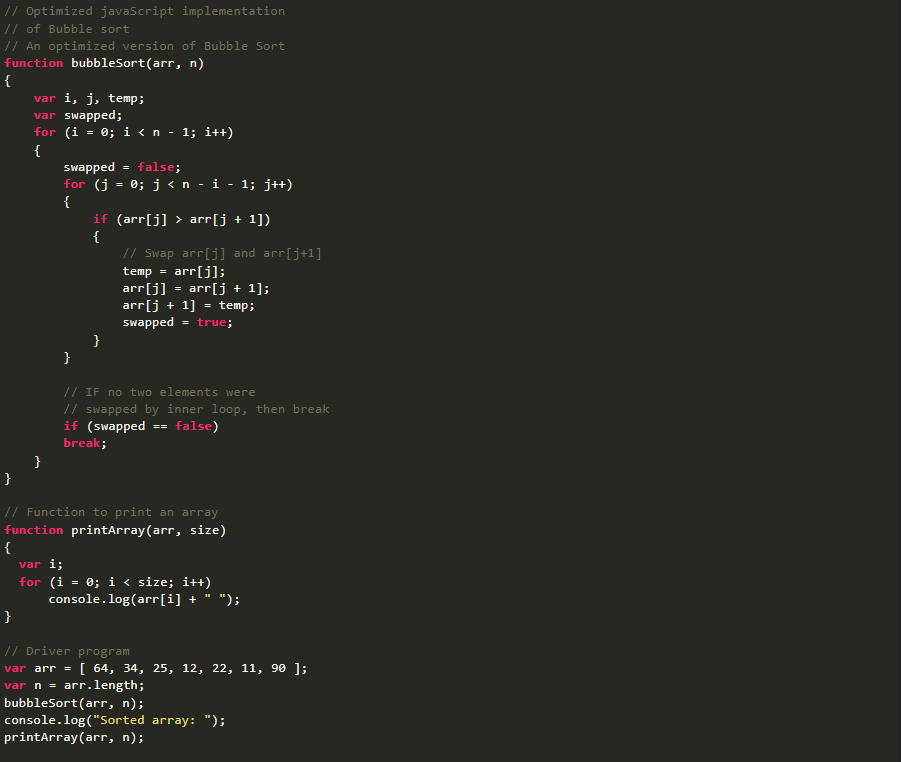
Basic Principle:
- Bubble sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm.
- It operates by continuously iterating through a list of elements and comparing adjacent elements.
Efficiency and Complexity:
- Bubble sort has a time complexity of O(n^2), where 'n' represents the number of elements in the list.
- Its efficiency decreases significantly with larger datasets, making it inefficient for extensive collections of elements.
Iterative Process:
- Bubble sort proceeds through the list multiple times, each pass gradually positioning the largest (or smallest) unsorted element to its correct place.
- With each iteration, larger (or smaller) elements "bubble up" or move toward the end (or beginning) of the list.